
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create systems and machines capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence. Here’s a general overview:
Type of Artificial Intelligence
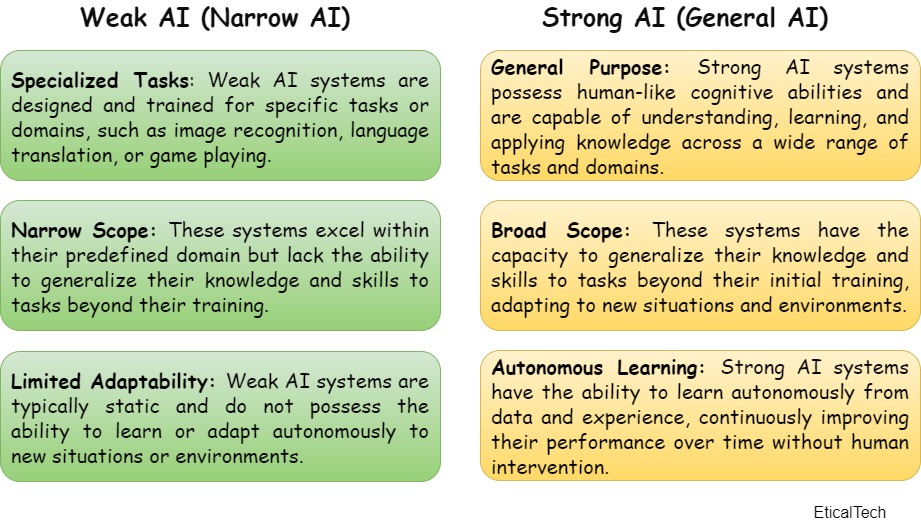
Weak AI (Narrow AI): This type of AI is designed and trained for a specific task, such as image recognition, natural language processing, or playing chess. Weak AI systems excel at their specific tasks but lack the ability to generalize beyond their training, also Weak AI relies on human interference to define the parameters of its learning algorithms and to provide relevant training data to ensure accuracy.
Strong AI (General AI): Strong AI refers to AI systems that possess human-like cognitive abilities and can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks. Strong AI can perform a variety of functions, possibly teaching itself how to solve new problems. It is used in the most diverse areas of everyday life. One of its recent applications is aimed at the creation of various intellectual works as particular pictorial works or music.
Key Techniques and Approaches
Machine Learning: Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Techniques include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning (Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural).
Automation and robotics: empowers machines to learn, adapt, and perform tasks autonomously, enhancing efficiency and precision, AI enables robots to perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute complex actions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP focuses on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It encompasses tasks such as sentiment analysis, language translation, and chatbots.
Computer Vision: Computer vision involves enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from the real world, such as images and videos. Applications include object recognition, image classification, and autonomous vehicles.
Applications
Healthcare: AI is used in medical imaging, disease diagnosis, personalized treatment planning, drug discovery, and patient monitoring.
Finance: AI is applied in fraud detection, algorithmic trading, risk assessment, customer service, and make investiment decision.
Retail and E-commerce: AI is used for recommendation systems, demand forecasting, customer segmentation, and supply chain optimization.
Transportations: AI powers self-driving cars and drones, enabling them to perceive their environment, make decisions, navigate safely and traffic management.
Manufacturing: AI is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, process optimization, and robotics in manufacturing facilities.
Entertainment: AI is used in gaming, content recommendation, personalized marketing, and content creation (e.g., music composition, artwork generation).
Education: can be used to create personalized learning for students. AI can identify areas where the student needs additional support and provide targeted instruction.
With this article we wanted to outline the general aspects of artificial intelligence and then analyze each individual aspect and approach.
Top image from freepik
